OBE Process
The traditional teaching system in education focuses on teachers’ inputs and presume that learning has occurred. The Outcome Based Education (OBE) is focusing on “what the students are capable of doing”.
The OBE is learner citric approach in which, it’s not important what we teach,
but it’s important what student learn

Since OBE focusses on student competency, it concentrates on the outcomes or goals instead of just marks or scores. Therefore, the goals which could be a certain number of skills and knowledge that the learner should have at the end of the course. The assessment methods are defined to measure the achievement of these goals. The teachers take the role of being facilitators and mentors. Constructive feedback from the students also helps in reshaping the additional Value-added Programs (VAP) and activities to be given to the students as shown in Figure.

Attainment of Outcomes
- The Program Outcomes (POs) and Program Specific Outcomes (PSOs) are accomplished through curriculum
- Course Outcomes (COs) are defined for each course and they are mapped to POs and PSOs.
- A set of performance evaluation criteria is used for quantitative assessment of COs
- Thus, the attainment of COs provides evidence of attainment of POs and PSOs.
Measurement of Outcome Attainment
During the course of the programme, various measurement methods are used to measure the attainment of outcomes. The assessment of outcome attainment largely depends on the student’s performance output or marks obtained in final theory and practical examination, test, and submission of assignments which indicates students learning achievements. Therefore, it is necessary and important to carry out a proper attainment method in order to measure student learning achievement and to predict the student’s performance in future.
There are different ways to assess student learning. Different types of assessment approaches available and the different frame works to interpret the results are as follows:
· Continuous Internal Assessment (CIA) · Alternate Assessment Tools (AAT) · Mid-SEM Examination (MID-SEM) · End Semester Examination (ESE) · Laboratory Work (PR) · Mock Oral (OR) · Project work Presentation and Demo · Academic Audit Committee · IQAC Reviews · Course exit survey · Programme exit survey · Alumni survey · Employer survey · Course expert committee · Department Advisory Board (DAB) · Faculty meetings · Professional societies · Industrial Advisory Committee (IAC) |
Assessment Methods
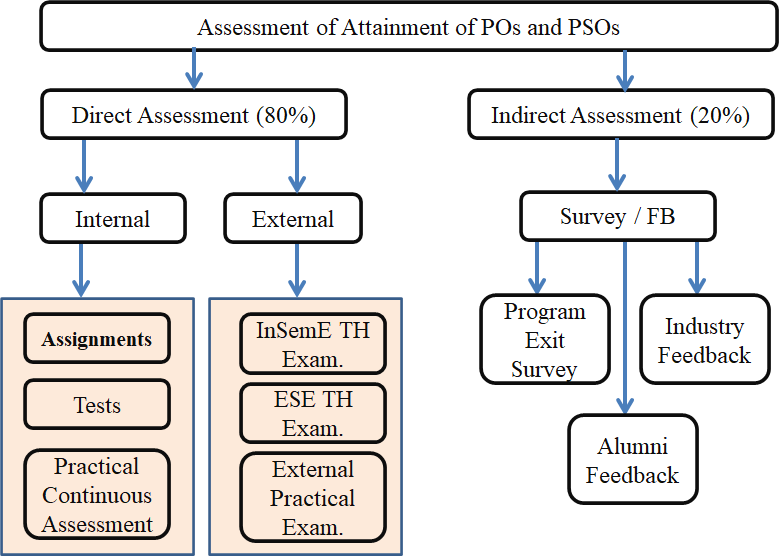
Different methods for Assessment, Evaluation and Measurement of POs/PSOs are broadly classified as:
- Direct Assessment methods
- Indirect Assessment methods
The details of methods are as shown in Figure
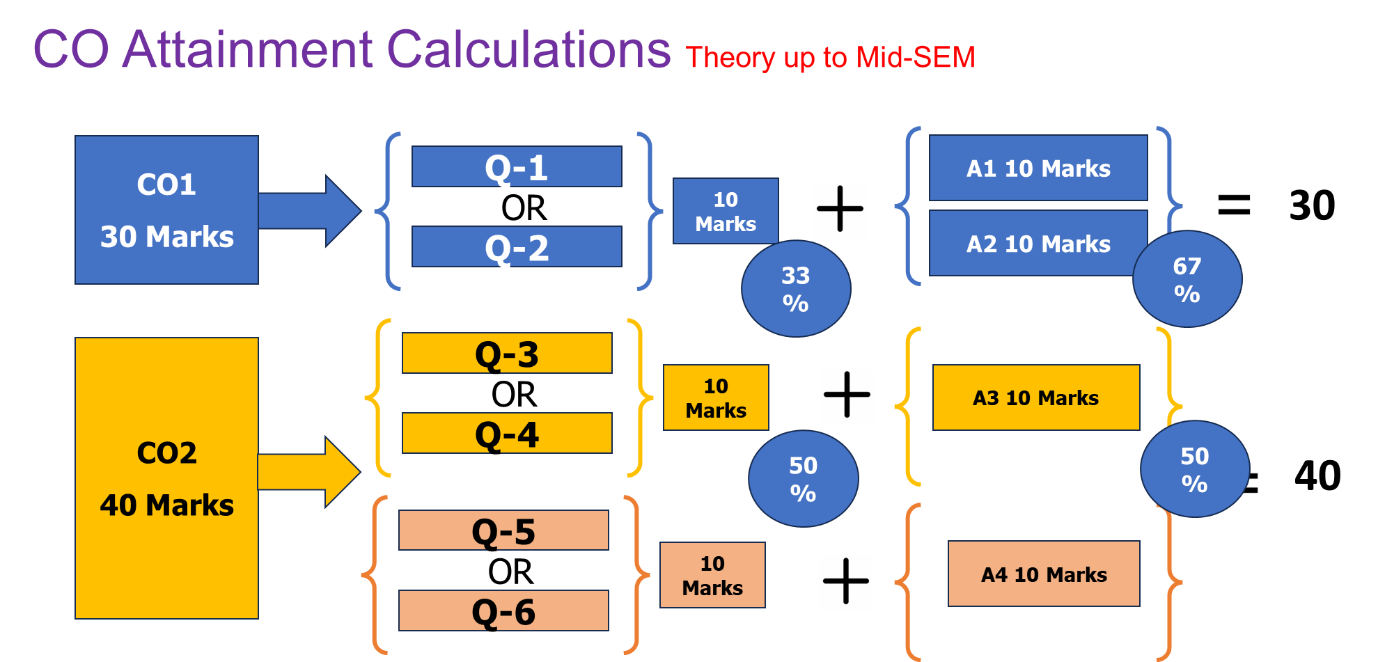
- Continuous Assessment: COs are assessed through Mid-SEMSPPU examination & Assignment Examinations, Home Assignments, Tests and Lab records. The COs are mapped against each question and CO analysis is carried out by faculty for each course and documented. The contribution of COs are assessed in high, moderate and low levels, towards the attainment of POs/PSOs.
- Mid-SEM Theory Examination: The SPPU conducts Mid-SEM Examination (In-SEME) for the first two units of the course curriculum. The marks assigned for this examination are 30.
- End-SEM Theory Examinations: The questions in End SEM examinations are tested pertaining to all COs, in varying Blooms Taxonomy Levels. The SPPU conducts End-SEM Examination (ESE) for the last four units of the course curriculum. The marks assigned for this examination are 70.
- End-SEM PR/OR Examinations: The SPPU conducts ESE for Practical Courses either Practical or Oral examination. The marks assigned for these examinations are 25 or 50.
- Laboratory Records: Both continuous evaluation (in terms of term work) and End SEM examinations (in terms of PR/OR ESE) are conducted to test the COs attainment.